 For more than six decades, a group known as the Poplar Islands Yacht Club (PIYC) has existed in our region; and, while the islands may have disappeared, PIYC remains dedicated to its mission of fostering camaraderie and maritime adventure through cruising adventures on and around Chesapeake Bay. Founded in 1961 as a means of fostering the fraternity of yachting, the club has weathered various challenges while leaving an indelible mark on Maryland’s boating culture.
For more than six decades, a group known as the Poplar Islands Yacht Club (PIYC) has existed in our region; and, while the islands may have disappeared, PIYC remains dedicated to its mission of fostering camaraderie and maritime adventure through cruising adventures on and around Chesapeake Bay. Founded in 1961 as a means of fostering the fraternity of yachting, the club has weathered various challenges while leaving an indelible mark on Maryland’s boating culture.The PIYC’s origins can be traced back to the late 1950s when an increasing number of yachtsmen from both the Eastern and Western Shores of Maryland began cruising to the quaint harbor nestled within the Poplar Islands. Presidents Franklin D. Roosevelt and Harry S. Truman even sought solace in these islands during the 1930s and ’40s, playing poker, feasting on crabs and oysters, and engaging in private meetings with Democratic leaders.
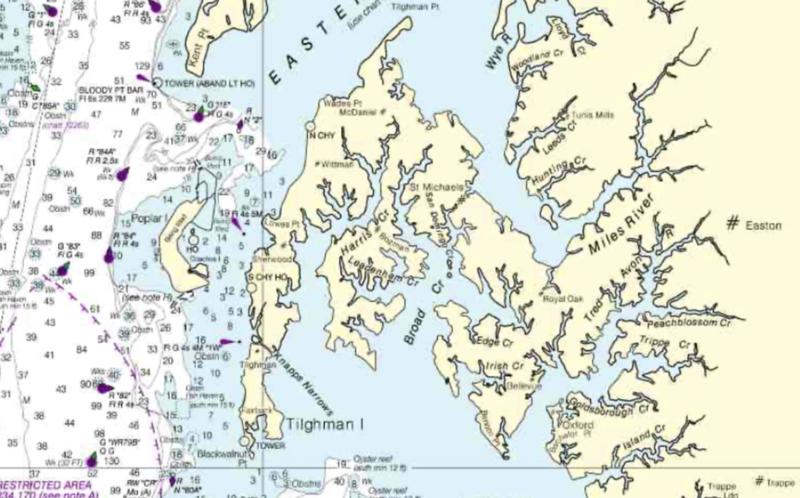
Following a fire that razed the main lodge in 1946, the islands changed hands multiple times until they found a new purpose under Daniel H. Hodgeman. Hodgeman rebuilt the lodge and transformed the islands into a seasonal hub for the Poplar Islands Yacht Club in the summer and a gun club in the fall and early winter.
With the lodge restored and additional buildings renovated, the PIYC grew in popularity. Yachts frequented the harbor, with regular visitors securing their own name boards and reserved slips on the 300-foot pier that led to deep waters in Poplar Harbor. The navigational challenge of reaching the pier was overcome by two World War I mines painted orange and repurposed as buoys.
However, financial difficulties eventually forced Hodgeman to sell the islands to Dr. George Elkins of Philadelphia, who later donated them to the Smithsonian Institution for conservation and use as a wildlife refuge.
Over the years, the islands faced the threat of erosion and the division of land masses due to heavy storms. Concerned with the islands’ conservation, the State of Maryland and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers collaborated in 1994 to restore them as a waterfowl and wildlife sanctuary. The project involved enlarging Poplar Island using dredged materials from the Chesapeake Bay and Baltimore Harbor.
For the PIYC, the changing landscape necessitated a shift in focus. In 1965, the club’s members decided against purchasing the islands due to their high cost. Instead, they opted for monthly rendezvous during the yachting season at other yacht clubs and waterfront homes, leading to more engaging and diverse experiences.
The club’s membership, once limited to 60 yachtsmen within a 250-mile radius of the Chesapeake Bay, experienced a transition from sail to powerboats and from wood to fiberglass. As new activities and destinations were incorporated into the club’s itineraries, cruises began including more overnight stays at marinas with various amenities, such as floating docks, pools, restaurants, and even yoga facilities.
In recent years, the PIYC has seen significant milestones. In 2021, for the first time in its history, a woman was elected Commodore, breaking the so-called “fiberglass ceiling.” Additionally, the club’s newsletter, once a mimeographed flyer, evolved into a digital publication called “Anchor Lines,” featuring vibrant color photos and shared links to members’ extensive Southbound cruises.


Tod Herrick says
I’d like To point out an error in an otherwise well written article. You say that the spoils from dredging in the Chesapeake Bay AND BALTIMORE HARBOUR were used to fill the newly reclaimed Poplar Island. While it is true they used the dredged materials from the Chesapeake Bay, they avoided using dredged materials from Baltimore Harbour and the Patapsco River due to the possible high levels of pollution and heavy metals in the bottom. This was to make a more pristine environment.
Dave Wheelan says
Poplar Island is an environmental restoration project located in the Chesapeake Bay in Talbot County, Maryland. The beneficial use project relies on dredged material collected from the approach channels to the Baltimore Harbor to restore lost remote island habitat within the Chesapeake Bay.